Ultrasound therapy is a widely used modality in physical therapy and rehabilitation. It involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to promote tissue healing, reduce pain, and improve joint mobility. This overview explores the principles behind ultrasound therapy, its techniques and applications, the benefits it may offer, as well as its limitations and the current state of research in this field.
What Is Ultrasound Therapy?
Ultrasound therapy utilizes sound waves with frequencies typically ranging from 0.8 to 3 MHz, which are transmitted into tissues through a transducer. These sound waves interact with biological tissues to produce thermal and non-thermal effects that may help accelerate healing, alleviate pain, and enhance tissue repair.
The Mechanisms of Action
There are two primary mechanisms through which ultrasound therapy is thought to work:
Application Methods
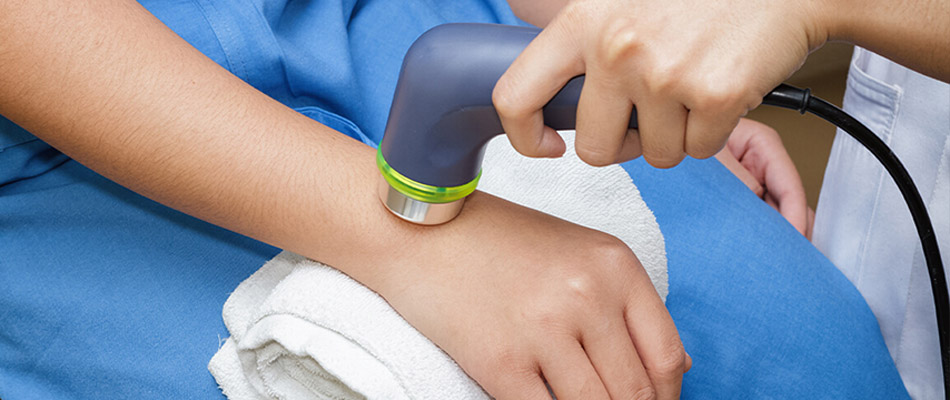
Ultrasound therapy is administered using a handheld transducer that is placed in contact with the skin over the treatment area. A coupling gel is applied to ensure efficient transmission of the sound waves. The transducer is then moved continuously over the affected area to ensure uniform energy delivery.
Key Treatment Parameters
Several parameters influence the effectiveness of ultrasound therapy:
Ultrasound therapy is used in a variety of clinical settings due to its potential benefits, which include:
Pain Relief
The thermal effects of ultrasound can help reduce pain by decreasing muscle spasms and alleviating joint stiffness. Increased blood flow from vasodilation also aids in reducing inflammation and pain associated with soft tissue injuries.
Enhanced Tissue Healing
The non-thermal effects, such as cavitation and acoustic streaming, are believed to stimulate cellular repair processes. This can accelerate the healing of injured tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Increased Range of Motion
By warming the tissues and increasing collagen extensibility, ultrasound therapy may improve the range of motion in joints affected by contractures or fibrosis. This is particularly beneficial for patients recovering from surgery or long-term immobilization.
Reduction of Edema and Inflammation
The mechanical effects of ultrasound can facilitate the removal of inflammatory mediators and improve lymphatic drainage. This, in turn, may help reduce swelling and inflammation in the affected area.
Muscle Relaxation
The gentle heating and subsequent relaxation of muscle fibers help reduce tension and spasm. This can be especially useful in chronic conditions where muscle tightness contributes to pain and functional limitations.
Ultrasound therapy is versatile and has been applied in treating a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions:
Soft Tissue Injuries
While ultrasound therapy offers numerous benefits, it also has limitations and contraindications that practitioners must consider:
Limitations
The body of evidence for ultrasound therapy includes a mix of clinical studies, randomized controlled trials, and systematic reviews. Key points include:
Patient Selection
Proper patient selection is crucial. Ultrasound therapy is best suited for patients with specific musculoskeletal conditions where the benefits of increased blood flow, tissue relaxation, and enhanced healing can be maximized. A thorough clinical evaluation helps determine whether a patient is an appropriate candidate.
Treatment Planning
Clinicians must tailor ultrasound therapy protocols to individual patient needs. Factors such as the depth and location of the injury, the desired therapeutic effect (thermal vs. non-thermal), and patient comfort all guide the selection of parameters.
Integration with Other Modalities
Ultrasound therapy is most effective when used as part of a multimodal rehabilitation program. Combining ultrasound with:
Future research in ultrasound therapy may focus on:
Ultrasound therapy is a versatile and widely used modality in the field of physical therapy and rehabilitation. By harnessing both thermal and non-thermal effects, it offers potential benefits such as pain relief, increased tissue healing, improved range of motion, and reduced inflammation. While its clinical application is generally safe and effective for many musculoskeletal conditions, careful patient selection, proper parameter adjustment, and integration with other therapeutic approaches are essential for optimizing outcomes.
Although some variability in research findings exists, ongoing studies continue to refine our understanding of ultrasound therapy and its underlying mechanisms. Future advancements in technology and protocol standardization may further enhance its role as a cornerstone of rehabilitative care.
For practitioners and patients alike, ultrasound therapy represents a valuable tool in the comprehensive management of musculoskeletal disorders. By combining clinical expertise with emerging research, healthcare providers can tailor treatment strategies that maximize the benefits of ultrasound therapy, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
This comprehensive overview provides detailed insight into the principles, techniques, benefits, and challenges of ultrasound therapy, serving as a valuable resource for patients, therapists, and clinicians aiming to optimize musculoskeletal rehabilitation.
BOOK APPOINTMENT